Explore leverage and payoff in futures trading for India 2025. Learn strategies, risks, and opportunities with expert insights and data-driven charts.
In 2024, the Indian derivatives market recorded a staggering ₹440 lakh crore in turnover on the National Stock Exchange (NSE), with futures trading being a key driver (Source: NSE Factbook). Leverage, the ability to control large positions with a small margin, is the cornerstone of futures trading, offering both high rewards and significant risks. Understanding leverage and the payoff structure is critical for retail and institutional investors looking to navigate the Indian futures market in 2025.
This blog post dives into leverage and payoff in futures trading, exploring macroeconomic drivers, sectoral opportunities, risks, and practical strategies for 2025. Backed by data from NSE, BSE, RBI, and expert insights from platforms like Economic Times and Bloomberg, we provide actionable insights, charts, and real-world examples. Whether you’re a beginner exploring futures or a seasoned trader optimizing returns, this guide will help you master leverage and payoff in India’s dynamic market.
2025 Macroeconomic Drivers of Futures Trading
Leverage and payoff in futures are influenced by broader economic conditions shaping India’s market in 2025.
GDP Growth and Market Sentiment
India’s projected GDP growth of 7.2% for FY25 (Source: RBI Monetary Policy Review, Dec 2024) supports bullish sentiment in futures markets. Strong domestic consumption and infrastructure spending drive trading volumes, though agricultural futures may face volatility due to monsoon uncertainties.
RBI Monetary Policy
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is expected to maintain a neutral stance, keeping the repo rate at 6.5% (Source: CMIE). Stable interest rates stabilize the cost of carry in futures pricing, but potential rate hikes could increase margins, affecting leverage levels.
Global Economic Factors
Global uncertainties, including U.S. Federal Reserve rate decisions and oil price volatility, impact futures markets. In 2024, Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) invested ₹2.1 lakh crore in Indian equities, including derivatives (Source: NSDL). A stronger U.S. dollar could reduce FPI flows, tightening liquidity in futures.
FPI and DII Dynamics
Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) invested ₹3.5 lakh crore in 2024, offsetting FPI volatility (Source: CDSL). Retail participation in futures grew 15%, driven by platforms like Zerodha (Source: SEBI). High DII and retail activity ensure liquidity, enabling leveraged positions.
Chart: Leverage Impact on Futures Margins (2024)
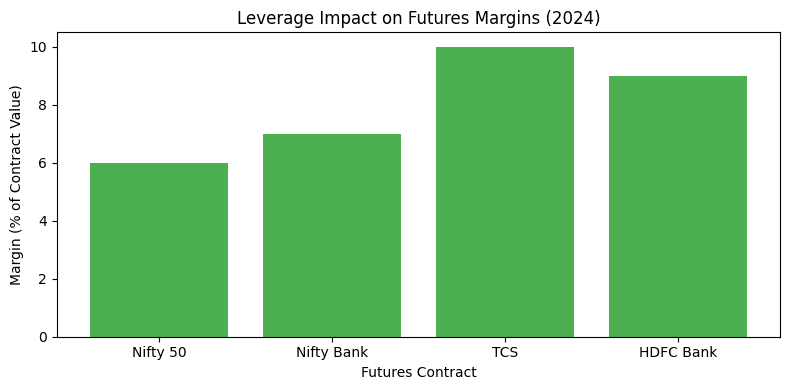
This bar chart compares margin requirements for key futures contracts in 2024, showing how leverage amplifies exposure.
- X-Axis: Contracts (Nifty 50, Nifty Bank, TCS, HDFC Bank).
- Y-Axis: Margin as a percentage of contract value (5-15%).
- Bars: Nifty 50 (6%), Nifty Bank (7%), TCS (10%), HDFC Bank (9%).
- Appearance: Green bars (#4CAF50) show margin percentages, highlighting lower margins for index futures due to higher liquidity.
Emerging Sectoral Trends for Futures Trading
Certain sectors offer high leverage and payoff potential in 2025 due to market dynamics and policy support.
Green Energy Futures
India’s net-zero goals and ₹1 lakh crore allocation for green hydrogen (Source: Economic Times, Jan 2025) make stocks like Adani Green Energy and Tata Power attractive for futures trading.
- Key Driver: Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes and renewable capacity targets.
- Opportunity: High volatility in energy stocks offers leveraged payoff potential.
Technology and IT Futures
The Nifty IT Index returned 19.8% in 2024 (Source: NSE), with companies like TCS and Infosys driving futures trading due to liquidity and earnings volatility.
- Key Driver: AI adoption and global IT contracts.
- Opportunity: Leverage TCS futures for short-term trades during earnings seasons.
Infrastructure Futures
Budget 2025’s ₹10 lakh crore capex fuels infrastructure stocks like Larsen & Toubro and Bharat Electronics (Source: Economic Times).
- Key Driver: Government spending on roads and defense.
- Opportunity: Leveraged positions in infrastructure futures benefit from order book growth.
Banking and Financial Services
BFSI stocks like HDFC Bank and Bajaj Finance are futures favorites due to high liquidity and sensitivity to RBI policies.
- Key Driver: Digital banking and fintech growth.
- Opportunity: Use leverage to capitalize on BFSI volatility post-RBI announcements.
Chart: Sectoral Futures Volatility (2024)
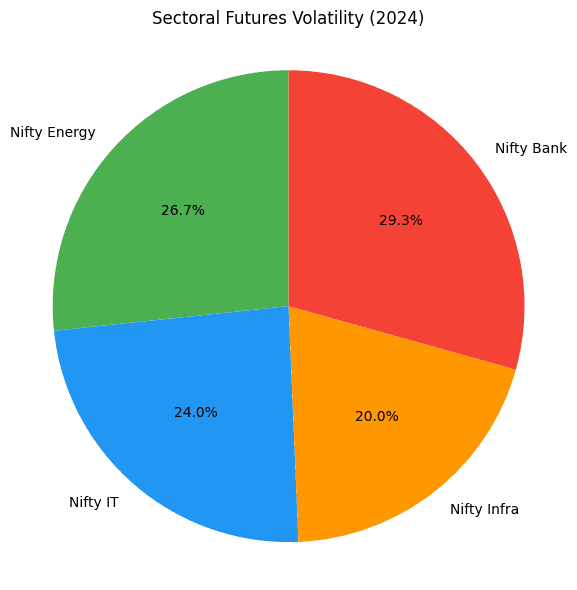
This pie chart shows volatility (standard deviation of daily returns) across sectors in 2024.
- Slices: Nifty Energy (20%), Nifty IT (18%), Nifty Infra (15%), Nifty Bank (22%).
- Appearance: Red (Nifty Bank, #F44336), blue (Nifty IT, #2196F3), green (Nifty Energy, #4CAF50), orange (Nifty Infra, #FF9800) slices, with Nifty Bank as the largest.
- Purpose: Highlights sectors with high volatility, ideal for leveraged futures trading.
Risks of Leverage in Futures Trading
Leverage amplifies both gains and losses, making risk management critical.
High Volatility
The India VIX averaged 15.2 in 2024, signaling potential turbulence (Source: NSE). Leveraged positions in volatile markets can lead to significant losses.
Margin Calls
Futures require margins (5-15% of contract value). A market drop can trigger margin calls, forcing traders to add funds or face square-offs (Source: SEBI).
Overvaluation Risks
Sectors like renewables (P/E: 80x) and IT (P/E: 28x) show high valuations (Source: BSE). A correction could erode leveraged payoffs.
Liquidity Risks
Low liquidity in mid-cap stock futures can hinder squaring off, locking in leveraged losses.
Chart: India VIX Trend (2020-2024)
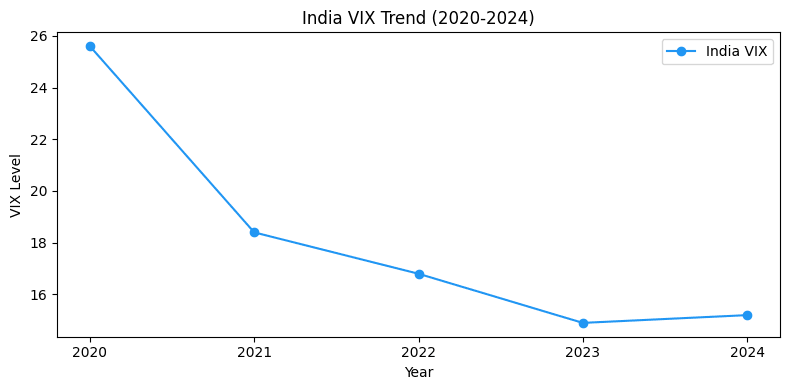
This line chart tracks the India VIX, illustrating volatility trends.
- X-Axis: Years (2020-2024).
- Y-Axis: VIX Level (10-30 range).
- Line: Blue line (#2196F3) showing VIX declining from 25.6 (2020) to 14.9 (2023), rising to 15.2 (2024).
- Purpose: Warns of increasing volatility risks for leveraged trades in 2025.
Top Opportunities with Leverage and Payoff in 2025
Disclaimer: The following are not trading tips but suggestions based on market trends. Consult a financial advisor before trading.
Stocks for Futures Trading
- TCS: High liquidity, ideal for leveraged short-term trades (lot size: 150, margin: ~10%).
- HDFC Bank: Stable fundamentals with policy-driven volatility (lot size: 550).
- Larsen & Toubro: Benefits from capex cycles (lot size: 300).
- Adani Green Energy: High volatility for aggressive traders (lot size: 200).
Index Futures
- Nifty 50 Futures: Low margin (6%) and high liquidity for leveraged bets (lot size: 25).
- Nifty Bank Futures: Sensitive to RBI policies, offering high payoff potential (lot size: 15).
Hedging with Futures
- Use Nifty 50 futures to hedge equity portfolios, reducing unsystematic risk.
- Pair futures with options (e.g., bull call spreads) to cap losses while leveraging gains.
- Maintain 10-15% cash reserves for margin requirements.
Table: Futures Contract Margins (2024)
| Contract | Lot Size | Margin (% of Contract Value) | Approx. Margin (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nifty 50 | 25 | 6% | 30,000 |
| Nifty Bank | 15 | 7% | 25,000 |
| TCS | 150 | 10% | 60,000 |
| HDFC Bank | 550 | 9% | 80,000 |
Source: NSE
Expert Opinions & Data-Backed Insights
Nilesh Shah, MD, Kotak AMC, states, “Leverage in futures can amplify returns, but without discipline, it’s a recipe for disaster. Focus on liquid contracts in 2025” (Source: Bloomberg, Jan 2025). Saurabh Mukherjea, Marcellus Investment Managers, notes, “BFSI and IT futures offer high payoff potential due to structural growth and volatility” (Source: Economic Times, Dec 2024).
NSE data shows futures turnover grew 12% in 2024, with Nifty 50 futures accounting for ₹120,000 crore daily (Source: NSE Factbook). The linear payoff structure of futures (gain/loss proportional to price movement) makes leverage a double-edged sword.
How Should a Retail Investor Navigate Leverage and Payoff in 2025?
Three Strategies for Beginners
- Start with Low Leverage: Trade one lot of Nifty 50 futures (margin: ~₹30,000) to limit risk. Learn more about futures basics.
- Use Stop-Losses: Set stop-losses at 2-3% of contract value to cap losses.
- Monitor Margins Daily: Ensure 1.5x margin coverage to avoid forced square-offs.
Portfolio Examples
- Conservative: 70% Nifty 50 futures, 20% debt, 10% cash.
- Balanced: 50% Nifty 50 futures, 30% stock futures (TCS, HDFC Bank), 20% cash.
- Aggressive: 60% stock futures (IT, infra), 30% Nifty Bank futures, 10% cash.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Over-Leveraging: Limit leverage to 5x to avoid margin calls.
- Ignoring Mark-to-Market (M2M): Monitor daily M2M settlements to manage cash flow.
- Chasing Volatility: Base trades on technical analysis, not market hype.
Practical Example: Leverage and Payoff with TCS Futures
Let’s apply the Zerodha Varsity example to 2025. On January 15, 2025, TCS announces cautious guidance, dropping its spot price by 3.5% to ₹4,200 (Source: NSE). The January 30, 2025, futures contract trades at ₹4,230 (lot size: 150, margin: 10%, ~₹60,000).
Scenario: You’re bullish, believing the drop is overblown. You buy one lot of TCS futures (contract value: ₹6,34,500) with ₹60,000 margin, leveraging ~10x.
Payoff Scenarios
- Price Rises: By January 30, TCS futures rise to ₹4,430. Payoff: ₹200/share (₹4,430 – ₹4,230) x 150 = ₹30,000 profit (50% return on margin).
- Price Falls: Futures drop to ₹4,030. Payoff: -₹200/share x 150 = -₹30,000 loss (50% loss on margin).
- Price Unchanged: No profit/loss at ₹4,230.
Squaring Off Early
On January 20, TCS futures hit ₹4,300. You square off, booking ₹70/share x 150 = ₹10,500 profit (17.5% return on margin). The position transfers to a counterparty, and margins are unblocked.
Chart: TCS Futures Payoff (Hypothetical)
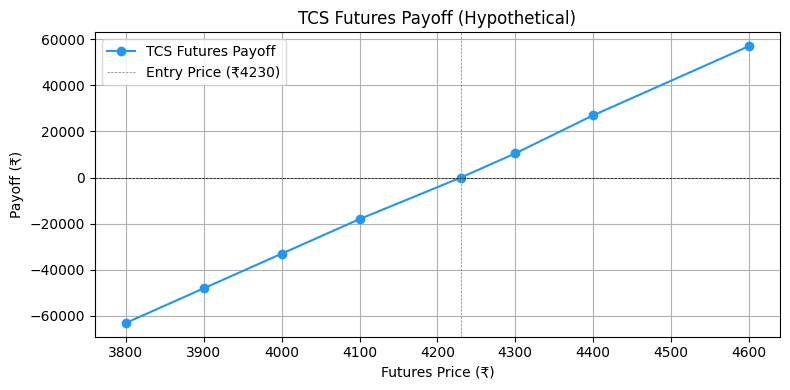
This line chart shows the payoff for one lot of TCS futures at different prices.
- X-Axis: Futures price (₹3,800-₹4,600).
- Y-Axis: Payoff (₹-60,000 to ₹60,000).
- Line: Linear slope showing profit/loss (e.g., ₹30,000 profit at ₹4,430, -₹30,000 loss at ₹4,030).
- Purpose: Illustrates the linear payoff structure of futures, amplified by leverage.
Conclusion
Leverage and payoff are central to futures trading in India for 2025, offering high returns but demanding strict risk management. With robust GDP growth, sectoral momentum in IT, BFSI, and infrastructure, and high liquidity in Nifty 50 futures, opportunities abound. However, volatility, margin calls, and overvaluation risks require caution. Key takeaways:
- Use low leverage (e.g., 5x) in liquid contracts like Nifty 50 or TCS.
- Set stop-losses and monitor M2M settlements.
- Hedge with index futures or options to limit downside.
- Stay informed with sources like NSE, RBI, and SEBI.
Retail and institutional investors can thrive by balancing leverage with discipline. Share your futures trading questions in the comments!
CTA: Want weekly futures trading insights? Subscribe to our newsletter for expert strategies, market updates, and trading tips!
References
Zerodha Varsity: Leverage & Payoff
Economic Times: Market Trends 2025
Moneycontrol: Derivatives Insights
SEBI Bulletins: F&O Regulations
NSE/BSE Factbooks: Market Data
CMIE Reports: Economic Outlook
RBI Monetary Policy Reviews: Monetary Policy
